June 2022 Issue
ISSN 2689-291X
ISSN 2689-291X
The Long & Short Of Calcium Abnormalities By ECG!
Description
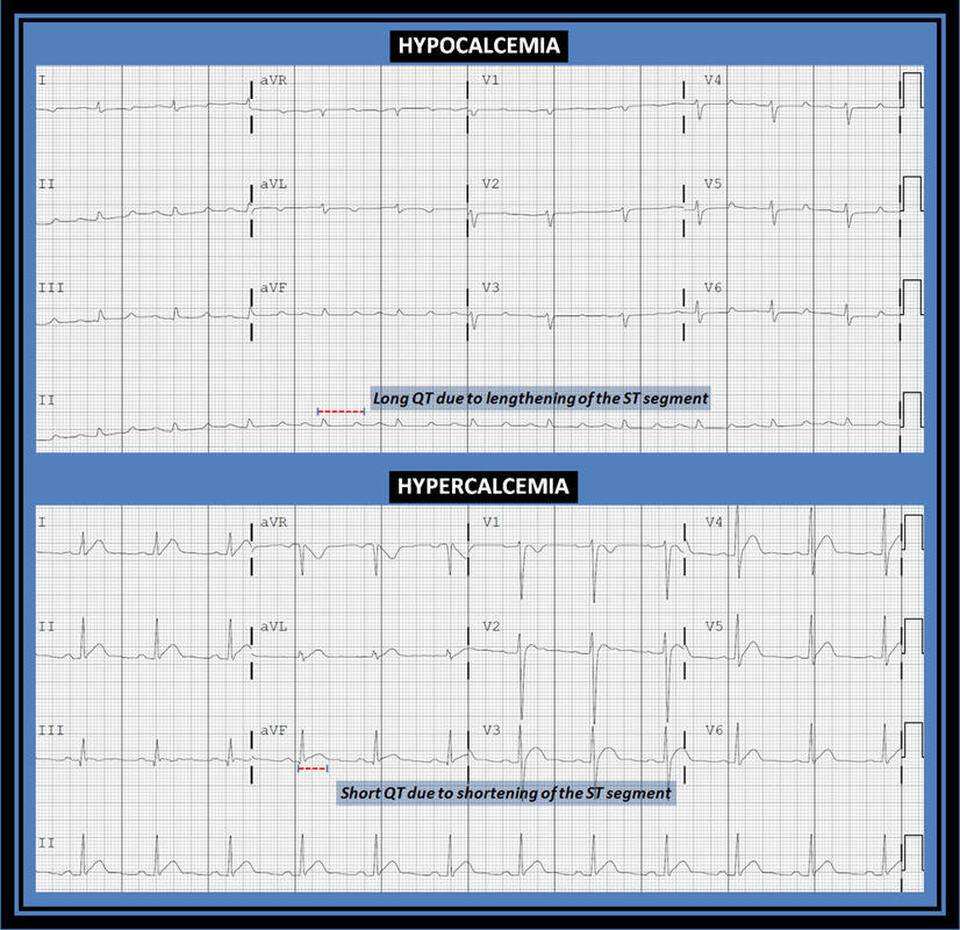
The above ECG shows the effect of hypocalcemia on the electrocardiogram (upper panel), resulting in QT prolongation predominantly due to lengthening of the ST segment. The effect of hypercalcemia on the ECG seen in the lower panel is shortening of the QT interval primarily due to shortening and near obliteration of the ST segment.
Discussion
Electrolyte abnormalities result in variable ECG abnormalities, some life-threatening, and should be promptly recognized and treated to avoid arrhythmias [1, 2].
Hypocalcemia results in a characteristic prolongation of the ST segment on the ECG proportional to the extent of low calcium level [3]. It increases phase 2 of the action potential duration which, in addition to prolonging the ST segment, can result in ST elevations suggestive of myocardial injury [4, 5]. Hypocalcemia usually does not alter the QRS complex or T wave [5].
Hypercalcemia results predominantly in shortening of the QT interval due to ST segment shortening [6]. Severe cases, however, may result in ECG changes mimicking myocardial injury [7, 8].
References
Authors:
Nikky Bardia, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Maulikkumar Patel, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Usman Sarwar, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Nupur Shah, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Rajasekhar Mulyala, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Mariam Riad, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Mustafeez Rahman, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
G. Mustafa Awan, M.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Christopher Malozzi, D.O.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
The above ECG shows the effect of hypocalcemia on the electrocardiogram (upper panel), resulting in QT prolongation predominantly due to lengthening of the ST segment. The effect of hypercalcemia on the ECG seen in the lower panel is shortening of the QT interval primarily due to shortening and near obliteration of the ST segment.
Discussion
Electrolyte abnormalities result in variable ECG abnormalities, some life-threatening, and should be promptly recognized and treated to avoid arrhythmias [1, 2].
Hypocalcemia results in a characteristic prolongation of the ST segment on the ECG proportional to the extent of low calcium level [3]. It increases phase 2 of the action potential duration which, in addition to prolonging the ST segment, can result in ST elevations suggestive of myocardial injury [4, 5]. Hypocalcemia usually does not alter the QRS complex or T wave [5].
Hypercalcemia results predominantly in shortening of the QT interval due to ST segment shortening [6]. Severe cases, however, may result in ECG changes mimicking myocardial injury [7, 8].
References
- Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA. Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities. J Emerg Med. 2004 Aug;27(2):153-60.
- El-Sherif N, Turitto G. Electrolyte disorders and arrhythmogenesis. Cardiol J. 2011;18(3):233-45.
- RuDusky BM. ECG abnormalities associated with hypocalcemia. Chest. 2001 Feb;119(2):668-9.
- Kukla P, Kulik M, Jastrzębski M. Severe hypocalcemia mimicking ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2017 Mar;22(2):e12401.
- Adeel MY, Clarke JD, Shetty S. Severe hypocalcemia mimicking acute inferior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2018 Nov 21;2018(12):omy103.
- Liu Y, Pérez-Riera AR, Barbosa-Barros R. Severe hypercalcemia from multiple myeloma as an acquired cause of short QT. J Electrocardiol. 2018 Nov-Dec;51(6):939-940.
- Nahass M, Sharma R, Penn J. Hypercalcemia-induced pancreatitis presenting with acute ST-elevations mimicking a myocardial infarction. Am J Emerg Med. 2016 Jun;34(6):1187.e1-2.
- Abugroun A, Tyle A, Faizan F. Hypercalcemia-Induced ST-Segment Elevation Mimicking Acute Myocardial Injury: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2020 Mar 16;2020:4159526.
Authors:
Nikky Bardia, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Maulikkumar Patel, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Usman Sarwar, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Nupur Shah, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Rajasekhar Mulyala, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Mariam Riad, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Mustafeez Rahman, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
G. Mustafa Awan, M.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Christopher Malozzi, D.O.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL