June 2023 Issue
ISSN 2689-291X
ISSN 2689-291X
Digitalis Electrocardiographic Effects: ST Scooping!
Description
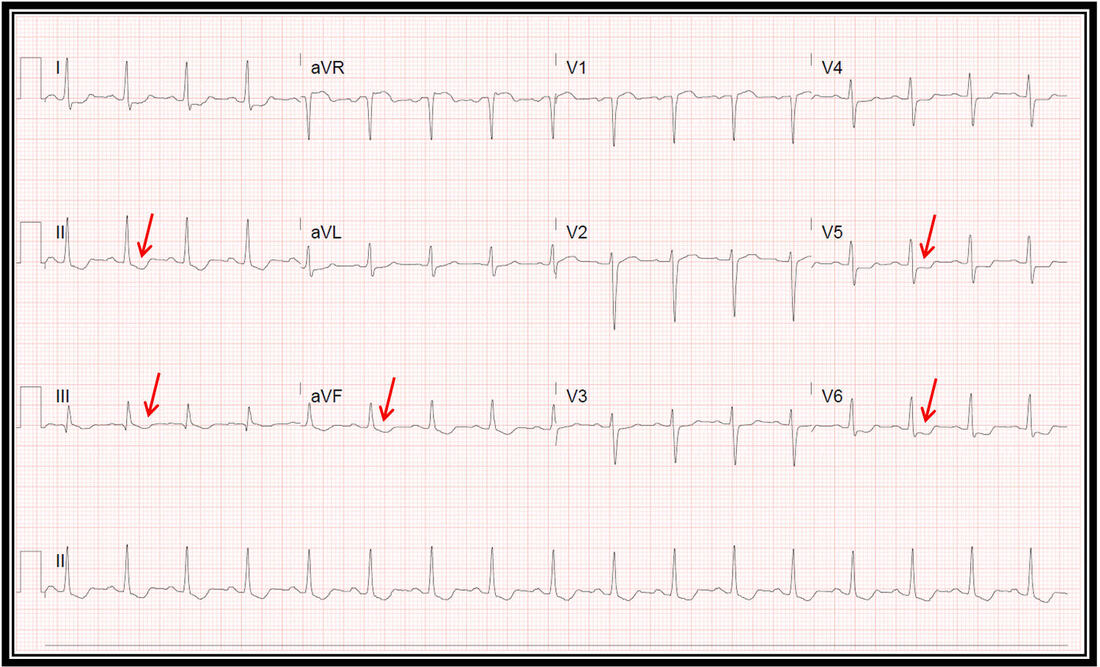
The above electrocardiogram (EKG) was obtained in a young patient with mild nausea treated with high dose digoxin to control fetal supraventricular tachycardia. Digoxin level was 2.3 ng/mL. Baseline EKG was normal. The red arrows show the typical scooping of the ST segments in the inferolateral leads seen in digitalis effect or toxicity which can mimic ischemia.
Discussion
Digoxin is an old medicine derivative of the Foxglove plant, with therapeutic benefit in heart failure and arrhythmia [1]. However, it has a narrow therapeutic index and has several potential toxicities [2]. Several drug-drug interactions have been documented with digoxin, increasing the risk of toxicity [3]. Digoxin is useful in the treatment of fetal supraventricular tachycardia in [4]. Various cardiac and noncardiac side effect of Digoxin therapy have been reported, mostly mild and self-limited [5].
References
Mariam Riad, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Rajasekhar Mulyala, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Nupur Shah, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Christopher Malozzi, D.O.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
The above electrocardiogram (EKG) was obtained in a young patient with mild nausea treated with high dose digoxin to control fetal supraventricular tachycardia. Digoxin level was 2.3 ng/mL. Baseline EKG was normal. The red arrows show the typical scooping of the ST segments in the inferolateral leads seen in digitalis effect or toxicity which can mimic ischemia.
Discussion
Digoxin is an old medicine derivative of the Foxglove plant, with therapeutic benefit in heart failure and arrhythmia [1]. However, it has a narrow therapeutic index and has several potential toxicities [2]. Several drug-drug interactions have been documented with digoxin, increasing the risk of toxicity [3]. Digoxin is useful in the treatment of fetal supraventricular tachycardia in [4]. Various cardiac and noncardiac side effect of Digoxin therapy have been reported, mostly mild and self-limited [5].
References
- Whayne TF Jr. Clinical Use of Digitalis: A State of the Art Review. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2018 Dec;18(6):427-440.
- Patocka J, Nepovimova E, Wu W, Kuca K. Digoxin: Pharmacology and toxicology-A review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;79:103400.
- Brown DD, Spector R, Juhl RP. Drug interactions with digoxin. Drugs. 1980 Sep;20(3):198-206.
- Gozar L, Gabor-Miklosi D, Toganel R, Fagarasan A, Gozar H, Toma D, Cerghit-Paler A. Fetal Tachyarrhythmia Management from Digoxin to Amiodarone-A Review. J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 2;11(3):804.
- Chimenea Á, García-Díaz L, Méndez A, Antiñolo G. Maternal effects induced by oral digoxin during treatment of fetal tachyarrhythmia: Case series and literature review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2021 Jan;256:354-357.
Mariam Riad, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Rajasekhar Mulyala, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Nupur Shah, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Christopher Malozzi, D.O.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL